In today’s busy world, convenience is more important than ever. Instacart steps in as the top platform transforming the way people buy groceries and everyday necessities from the comfort of their own homes. With millions of users worldwide, Instacart has become the go-to solution. It is for those who want the convenience of having groceries delivered right to their doorstep. Understanding Instacart goes beyond just user engagement; it’s about simplifying the shopping experience, saving time, and enhancing daily life. Find out in this article how Instacart makes money.
From delivery fees and service charges to strategic partnerships with grocery stores, Instacart has carefully developed a diverse range of revenue-generating avenues. Exploring the intricacies of Instacart’s business model not only illuminates its financial operations but also provides insights into its sustainability, growth trajectory, and impact on the retail landscape.
For a deeper dive into what Instacart is, check out a separate article by our team. This article delves into the business model canvas of Instacart, its revenue generation strategies, and how it makes money. Join us as we uncover the inner workings of Instacart’s revenue-generating mechanisms. Also, explore how this platform transforms convenience into currency.
Instacart Business Model
Instacart operates on a multifaceted business model that revolves around providing on-demand grocery delivery services. Customers browse through a wide selection of products on the Instacart platform and place orders, which are fulfilled by a network of personal shoppers. Instacart’s business model is centered around providing convenience to customers while leveraging technology and strategic partnerships to create value and drive revenue growth.
On-Demand Grocery Delivery Service
- Instacart offers customers the convenience of ordering groceries online through its platform.
- Customers browse through a wide range of products from local stores using the Instacart app or website.
- Orders are fulfilled by Instacart’s network of personal shoppers. They visit the designated stores, pick up the items, and deliver them to customers’ doorsteps.
Revenue Streams
- Delivery Fees: Customers pay a fee for the convenience of having their groceries delivered. The fee varies based on factors like order size and delivery time.
- Service Charges: Instacart imposes a service charge on each order to cover operational costs. For eg., platform maintenance and customer support.
- Markup on Products: Instacart may apply markups on the prices of products compared to their in-store prices. These contribute to additional revenue.
- Subscription Programs: Instacart offers subscription programs like Instacart Express, providing unlimited free deliveries. This is done for a fixed monthly or annual fee, generating recurring revenue.
Strategic Partnerships
- Instacart collaborates with grocery chains and brands. It allows them to list their products on the platform and reach a wider audience.
- Grocery stores partner with Instacart to expand their online presence and offer delivery services to their customers.
- Brands leverage Instacart’s advertising opportunities to increase visibility and drive sales.
Customer Experience
- Instacart prioritizes providing a seamless and user-friendly experience for customers through its digital platform and customer support services.
- The platform offers features like order tracking and customization options to enhance the shopping experience.
- Instacart’s focus on customer satisfaction contributes to customer loyalty and retention.
Expansion and Growth
- Instacart continuously seeks opportunities for expansion and growth, entering new markets and forming strategic partnerships to fuel its expansion.
- The company invests in technology and infrastructure to improve its operations and meet the growing demands of customers.
Innovation and Adaptation
- Instacart remains innovative and adaptive, introducing new features and services to meet the evolving needs of customers.
- The company explores new revenue streams and business opportunities to stay competitive in the dynamic grocery delivery market.
Instacart Business Model Canvas
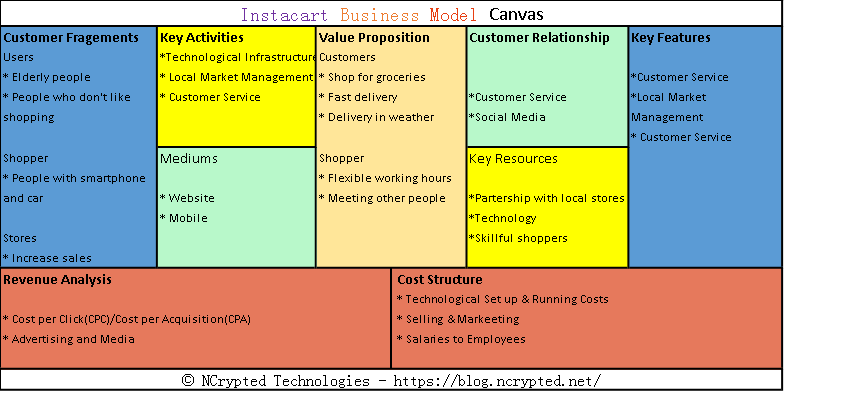
Key Partnerships
- Grocery Stores: Instacart partners with various grocery chains and independent stores. This offers a wide selection of products to its customers.
- Personal Shoppers: Instacart relies on a network of personal shoppers who fulfill orders and deliver groceries to customers. These shoppers are independent contractors who work with Instacart to provide timely and efficient service.
Key Activities
- Order Fulfillment: Instacart’s key activity is fulfilling customer orders by sourcing products from partner stores and delivering them to customers’ doorsteps.
- Platform Maintenance: Instacart maintains its digital platform, including its website and mobile app, to ensure seamless order placement and tracking.
- Customer Support: Instacart provides customer support services to address any issues or concerns that may arise during the shopping and delivery process.
Key Resources
- Technology Infrastructure: Instacart relies on technology to power its platform, including algorithms for order routing and scheduling, as well as customer-facing interfaces for order placement and tracking.
- Personal Shoppers: The network of personal shoppers is a key resource for Instacart, as they play a crucial role in fulfilling orders and delivering groceries to customers.
- Data and Analytics: Instacart leverages data and analytics to optimize its operations, improve customer experiences, and identify opportunities for growth and expansion.
Value Propositions
- Convenience: Instacart offers unparalleled convenience by allowing customers to order groceries online and have them delivered to their doorstep in as little as an hour.
- Selection: Instacart provides access to a wide selection of products from multiple stores, giving customers the flexibility to shop for groceries from their favorite retailers in one place.
- Time Savings: By outsourcing the task of grocery shopping to Instacart, customers can save time and focus on other priorities in their lives.
Customer Segments
- Busy Professionals: Instacart appeals to busy professionals who may not have the time or inclination to visit the grocery store regularly.
- Families: Families with young children or hectic schedules appreciate the convenience of Instacart for simplifying their grocery shopping experience.
- Elderly or Disabled Individuals: Instacart serves elderly or disabled individuals who may have difficulty physically going to the store but still want access to fresh groceries.
Customer Relationships
- User Experience: Instacart prioritizes providing a seamless and user-friendly experience for its customers through its digital platform.
- Customer Support: Instacart offers responsive customer support to address any questions or concerns that customers may have before, during, or after their shopping experience.
Channels
- Digital Platform: Instacart primarily operates through its digital platform, which includes its website and mobile app, allowing customers to place orders and track deliveries.
- Marketing and Advertising: Instacart utilizes marketing and advertising channels to raise awareness of its service and attract new customers, including online advertising, social media, and partnerships with influencers.
Revenue Streams
- Delivery Fees: Instacart charges customers a delivery fee for each order, which varies based on factors such as the size of the order and the delivery time selected by the customer.
- Service Fees: Instacart applies a service fee to each order to cover operational costs associated with providing its service.
- Markup on Products: In some cases, Instacart may apply markups to the prices of products compared to their in-store prices, allowing the company to generate additional revenue.
How does Instacart make money?
Instacart employs a multifaceted approach to generate revenue, leveraging various streams within its business model:
- Delivery Fees: One of the primary sources of revenue for Instacart is delivery fees. Customers pay a fee for the convenience of having their groceries delivered to their doorstep. The delivery fee varies based on factors such as the size of the order and the delivery time chosen by the customer. Additionally, Instacart offers an Express Membership program, where subscribers pay a monthly or annual fee in exchange for unlimited free deliveries on orders above a certain threshold.
- Service Fees: Instacart charges a service fee on each order, which helps cover the operational costs of the platform. This fee is typically a percentage of the total order amount and varies depending on factors such as the location and the size of the order.
- Markups on Products: In some cases, Instacart applies markups to the prices of products compared to their in-store prices. These markups are disclosed to customers, and the amount can vary depending on the item and the store. This strategy allows Instacart to generate additional revenue while still providing value and convenience to its customers.
- Partnerships and Advertising: Instacart earns revenue through partnerships with grocery stores and advertising opportunities for brands. Grocery stores pay Instacart to be listed on the platform and to have their products featured, increasing visibility to shoppers. Brands can also pay for advertising space within the Instacart app, allowing them to reach a targeted audience of grocery shoppers.
- Instacart Pickup: In addition to delivery services, Instacart offers a pickup option where customers can order groceries online and pick them up at the store. While this service typically has lower fees than delivery, it still contributes to Instacart’s overall revenue stream.
Instacart Funding Rounds
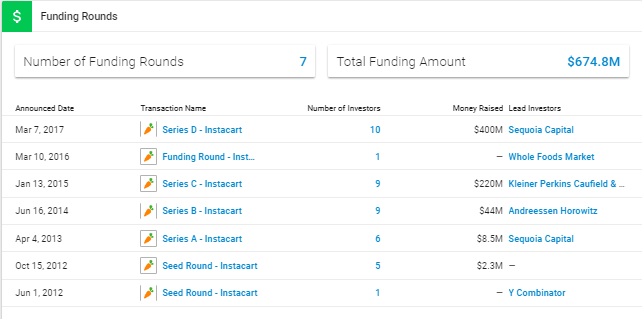
Seed Round (2012): Instacart was founded in 2012 by Apoorva Mehta. The company initially raised seed funding from various investors to kickstart its operations and develop its platform.
Series A Round (2013): In 2013, Instacart raised its Series A funding round, led by Sequoia Capital. This round of funding enabled Instacart to scale its operations and expand into new markets.
Series B Round (2014): Building on its early success, Instacart secured additional funding in its Series B round in 2014. The round was led by Kleiner Perkins and included participation from existing investors like Sequoia Capital.
Series C Round (2014): Later in 2014, Instacart raised another round of funding, known as the Series C round. This round was led by Andreessen Horowitz and included participation from existing investors. The funding helped fuel Instacart’s rapid expansion across North America.
Series D Round (2015): Instacart continued to attract significant investment in 2015 with its Series D funding round. The round was led by Coatue Management and included participation from prominent investors such as Thrive Capital and Dragoneer Investment Group.
Series E Round (2017): Instacart raised a substantial amount of capital in its Series E funding round in 2017. The round was led by Coatue Management and included investment from several other investors, bringing Instacart’s valuation to over $3 billion.
Additional Funding Rounds:
In the years following its Series E round, Instacart continued to raise additional funding from both new and existing investors. These funding rounds supported the company’s ongoing expansion efforts and technological advancements.
Strategic Partnerships and Investments:
In addition to traditional funding rounds, Instacart has formed strategic partnerships and received investments from major players in the retail and technology industries. For example, Instacart partnered with major grocery chains like Kroger and received investments from companies like Alibaba and Amazon.
Instacart Revenue Model
Delivery Fees
At the core of Instacart’s revenue model lies its delivery fees. Customers gladly pay a nominal fee for the luxury of having groceries delivered to their doorstep. Whether it’s a last-minute craving or a weekly stock-up, Instacart’s delivery fees serve as a reliable revenue stream, ensuring convenience comes at a cost.
Service Charges
In addition to delivery fees, Instacart imposes service charges on each order. These charges contribute to covering operational costs, including platform maintenance, customer support, and payment processing. By leveraging service charges, Instacart maintains its operational excellence while bolstering its bottom line.
Strategic Partnerships
Instacart’s revenue model thrives on strategic partnerships with grocery chains and brands. These partnerships not only expand Instacart’s product offerings but also serve as a lucrative revenue stream. Grocery stores pay Instacart for listing their products on the platform, while brands capitalize on advertising opportunities to enhance visibility and drive sales.
Subscription Programs
Instacart’s subscription programs, such as Instacart Express, offer customers unlimited free deliveries for a fixed monthly or annual fee. While providing value to customers, these programs also bolster Instacart’s revenue stream through recurring subscriptions. By fostering customer loyalty, Instacart secures a steady stream of revenue while delivering unparalleled convenience.
Instacart Competitors
Amazon Fresh / Amazon Prime Now: Amazon offers grocery delivery services through its Amazon Fresh and Amazon Prime Now platforms. With a vast selection of products and the convenience of Prime membership, Amazon poses a significant challenge to Instacart.
Walmart Grocery: Walmart Grocery allows customers to order groceries online and either pick them up at a nearby Walmart store or have them delivered to their doorstep. Walmart’s extensive network of stores and competitive pricing make it a formidable competitor to Instacart.
Shipt: Shipt is a grocery delivery service owned by Target. It offers same-day delivery of groceries and household essentials from various retailers, including Target, Costco, and CVS. Shipt’s focus on fast delivery and membership-based pricing model competes directly with Instacart.
DoorDash: While primarily known for food delivery, DoorDash has expanded into grocery delivery through partnerships with various retailers. With its extensive delivery network and competitive pricing, DoorDash poses a threat to Instacart in the on-demand delivery space.
Learn more about food delivery app development.
Postmates: Postmates, now owned by Uber, offers on-demand delivery of groceries and other goods from local stores. With its broad range of available products and competitive pricing, Postmates competes with Instacart for market share in the grocery delivery industry.
Grocery Store Chains: Many grocery store chains, such as Kroger, Safeway, and Albertsons, offer their own in-house delivery services, competing directly with Instacart. These chains leverage their existing infrastructure and customer base to provide convenient delivery options to customers.
Local and Regional Delivery Services: In addition to national competitors, Instacart competes with local and regional grocery delivery services that operate in specific geographic areas. These services often cater to niche markets or offer specialized products, posing a localized challenge to Instacart.
How does Instacart make money
As we conclude our exploration into Instacart’s business model and its place within the competitive landscape of grocery delivery, it becomes evident that Instacart has carved out a unique niche in the market. With its user-friendly platform, extensive network of personal shoppers, and strategic partnerships with grocery chains and brands, Instacart has revolutionized the way people shop for groceries and everyday necessities.
As Instacart continues to innovate and expand its offerings, its commitment to customer satisfaction and operational excellence remains unwavering. With a solid foundation built on a diverse range of revenue streams and a relentless pursuit of growth and adaptation, Instacart is poised to shape the future of grocery delivery and redefine the way people access essentials in the digital age.
So, whether you’re a busy professional, a parent juggling multiple responsibilities, or someone simply seeking convenience in everyday life, Instacart is here to deliver—literally and figuratively—making grocery shopping more accessible, efficient, and enjoyable for all.
How to Start an online grocery delivery app like Instacart?
After going through these interesting facts about the Instacart business model and how it makes money if you also want to build a similar app, check out our Instacart clone development service and connect with our team to discuss your business.